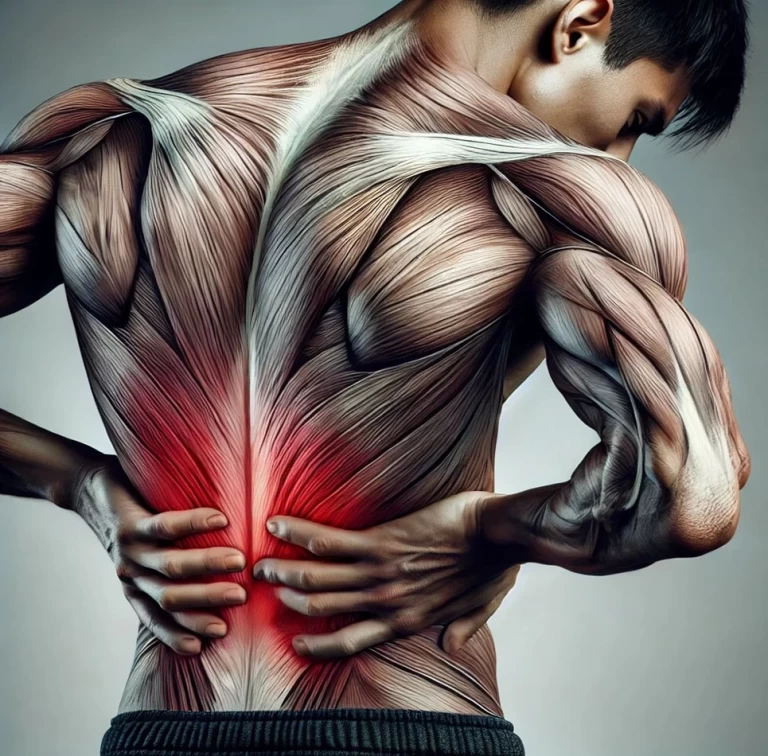
Pain is a common complaint that affects people of all ages and can arise from various causes. One of the most challenging aspects of pain management is determining whether the source of discomfort is muscle or nerve-related.
Understanding the distinction between muscle and nerve pain is crucial not only for diagnosis but also for determining the most effective treatment. Chiropractic care has emerged as a holistic approach to managing both muscle and nerve pain without the need for invasive procedures or medications. This article aims to explore the differences between muscle and nerve pain and how chiropractic care can offer relief.
By downloading the Digital Patient Chart mobile app you can better control your patient portal.
Introduction: Understanding Pain and Its Origins
Pain can be broadly classified into two categories: musculoskeletal pain, which involves muscles, bones, and joints, and neuropathic pain, which involves nerves. While muscle and nerve pain can sometimes overlap, each has distinct characteristics, symptoms, and treatments. Differentiating between these types of pain is critical for effective management and recovery.
Muscle pain typically arises from strain, overuse, or injury to the muscles or their associated structures, such as tendons and fascia. It often feels dull, aching, or tender. In contrast, nerve pain, also known as neuropathic pain, is typically the result of damage or irritation to the nerves. It is often described as sharp, shooting, or burning and can be associated with sensations of numbness or tingling.
Key Differences Between Muscle and Nerve Pain
To effectively manage pain, it is essential to identify whether it originates from muscles or nerves. Here are some of the primary distinctions between the two:
Nature of Pain: Muscle pain often feels like a deep ache or soreness. It is typically localized to the affected area and may worsen with movement. Nerve pain, on the other hand, tends to be sharp, electric, or burning, and it can radiate along the course of the affected nerve.
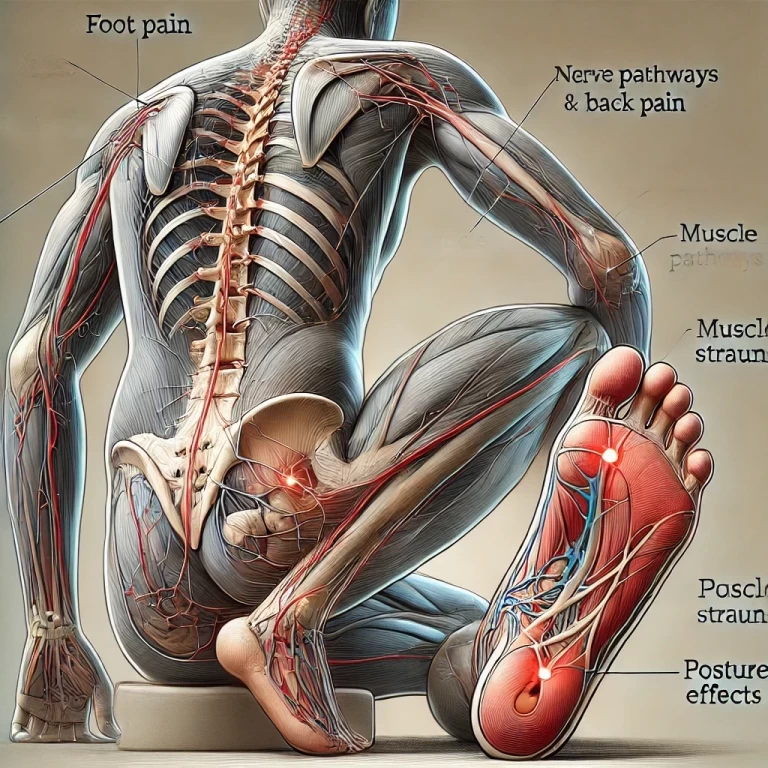
Pain Onset: Muscle pain is usually associated with physical activity, strain, or injury. It can also result from conditions like fibromyalgia or myofascial pain syndrome. Nerve pain may arise suddenly or progressively, often as a result of nerve compression, irritation, or damage due to conditions such as sciatica, herniated discs, or diabetic neuropathy.
Accompanying Symptoms: Muscle pain is often accompanied by stiffness, swelling, or weakness in the affected muscle group. Nerve pain, however, may come with sensations like numbness, tingling (paresthesia), or hypersensitivity to touch.
Radiation of Pain: While muscle pain is usually localized, nerve pain can radiate or travel along the path of the nerve. For example, sciatic nerve pain may extend from the lower back down to the legs.
Response to Treatment: Muscle pain typically responds well to rest, physical therapy, and chiropractic adjustments aimed at relaxing the muscles and improving joint function. Nerve pain often requires treatments that focus on reducing inflammation, decompressing the nerve, or addressing underlying causes like a slipped disc or spinal misalignment.
How Chiropractic Care Can Help Muscle and Nerve Pain
Chiropractic care offers a non-invasive, holistic approach to pain management. Chiropractors specialize in diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal disorders, including conditions that affect the muscles, nerves, and joints. Here’s how chiropractic care can benefit both muscle and nerve pain:
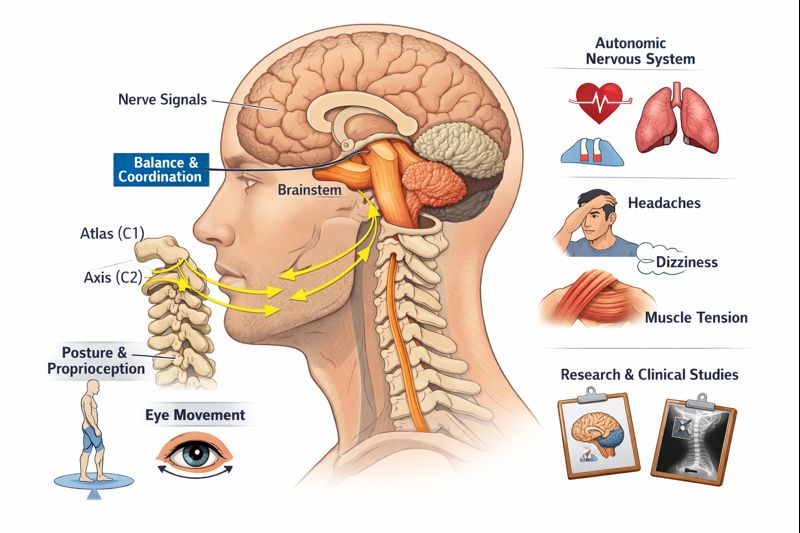
Spinal Adjustments for Nerve Pain: Nerve pain is often associated with spinal issues such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or nerve compression. Chiropractic adjustments can help realign the spine, reducing pressure on the affected nerves and alleviating pain. For instance, sciatica, a common form of nerve pain, is often treated through adjustments that reduce pressure on the sciatic nerve.
Therapeutic Exercises: Chiropractors often recommend specific exercises to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility. Strengthening weak muscles and improving posture can help prevent recurrent muscle strain and reduce the likelihood of developing nerve pain.
Lifestyle and Ergonomic Adjustments: Chiropractors frequently advise patients on lifestyle changes, such as proper posture, ergonomic improvements, and stress management techniques. These recommendations can help prevent the recurrence of muscle and nerve pain, especially in individuals with jobs that involve repetitive motions or prolonged periods of sitting.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications of Chiropractic Care
Numerous case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of chiropractic care in treating both muscle and nerve pain:
Sciatica Relief: In one case, a patient suffering from sciatica—a form of nerve pain caused by compression of the sciatic nerve—experienced significant relief after a series of spinal adjustments. The chiropractic treatment focused on realigning the lumbar vertebrae to reduce nerve compression, leading to a reduction in pain and improved mobility.
Neck Pain and Tension Headaches: Another case involved a patient with chronic neck pain and tension headaches, a common form of muscle pain. Chiropractic adjustments and soft tissue therapy helped alleviate the muscle tension, reducing the frequency and severity of the headaches.
Chiropractic Care vs. Other Treatments: Why Choose Chiropractic?
While conventional treatments for muscle and nerve pain often involve medications, chiropractic care offers a drug-free alternative. Chiropractic treatment focuses on the underlying causes of pain, providing long-term relief rather than temporary symptom management. Unlike surgery or invasive procedures, chiropractic care is non-invasive and typically has fewer risks and side effects.
Additionally, chiropractic care emphasizes whole-body wellness. By addressing factors such as posture, ergonomics, and lifestyle, chiropractors aim to prevent future episodes of pain and improve overall quality of life.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Treatment for Muscle and Nerve Pain
Whether you're dealing with muscle or nerve pain, it's essential to seek the right treatment to prevent the condition from worsening. Chiropractic care offers a comprehensive approach to pain management that addresses both the symptoms and the underlying causes of discomfort.
If you're experiencing pain and are unsure whether it's muscle or nerve-related, a consultation with a chiropractor can help you determine the source of your pain and the most appropriate course of treatment. Chiropractic care not only alleviates pain but also promotes long-term healing and improved well-being.






Leave a comment